

This study aimed to evaluate the impact of the CARTO Univu module on procedural safety and fluoroscopy in a wide spectrum of cardiac arrhythmias as compared to the use of the 3D-mapping system CARTO3 (Biosense Webster) alone in children. The application of CARTO Univu has been shown to further reduce fluoroscopy in adults ( 3), however, there are few studies about the use of this new technology on children. It could reduce fluoroscopy during the procedure.
CARTO SYSTEM SOFTWARE
“Fluoroscopy integrated 3D mapping”, a new 3D non-fluoroscopic navigation system software (CARTO Univu Module of CARTO3 system, Biosense Webster), was developed and allows electro-anatomical localization of diagnostic and ablation catheters in pre-recorded x-ray images or non-gated x-ray videos. Some new technologies for non-fluoroscopic visualization of the catheter are desirable. Concerns about children and involved medical staff being exposed to radiation during the procedure should not be ignored. Radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFCA) has become the main treatment for tachyarrhythmias in children in the past ten years ( 1, 2). ③ In the C3U group, the fluoroscopy during VAs ablation was lower than that of other arrhythmias ( P < 0.05).Ĭonclusion: The usage of the “novel image integration technology” CARTO Univu might be safe and effective in RFCA for a wide spectrum of tachyarrhythmias in children, which could significantly reduce fluoroscopy and has a more prominent advantage for VAs ablation. Corresponding to the fluoroscopy time, the fluoroscopy dose was also reduced significantly. ② The CARTO Univu reduced radiation exposure: fluoroscopy time: AVRT C3: 8.5 ± 7.2 min vs. Results: ① There was no significant difference in the acute success rate, recurrence rate, and complication rate between the C3 and C3U groups. The arrhythmias were atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT, n = 78), atrioventricular node reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT, n = 35), typical atrial flutter (AFL, n = 12), atrial tachycardia (AT, n = 20) and ventricular arrhythmias. The CARTO Univu was used for mapping and ablation in 200 cases (C3U group), and the CARTO3 was used in 200 cases as the control group (C3 group). Methods: The data of children with tachyarrhythmias who underwent RFCA from June 2018 to December 2021 were collected. In the present study, we analyzed the impact of the CARTO Univu on procedural safety and fluoroscopy in a wide spectrum of tachyarrhythmias as compared with CARTO3 alone. However, there are few studies about the use of this new technology on children.
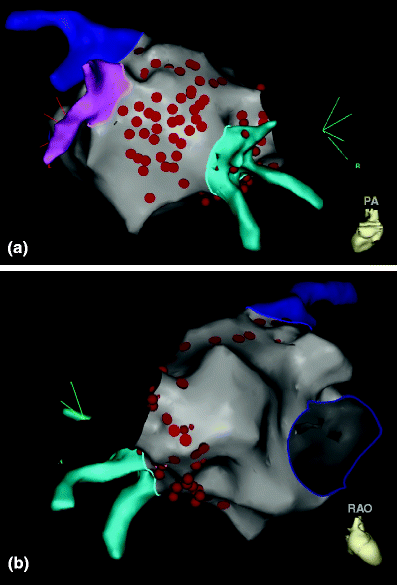
“Fluoroscopy integrated 3D mapping”, a new 3D non-fluoroscopic navigation system software (CARTO Univu Module) could reduce fluoroscopy during the procedure. Objective: Radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFCA) has evolved into an effective and safe technique for the treatment of tachyarrhythmia in children. 2Department of Pediatrics, Heart Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Tsinghua University, Beijing, China.1Department of Cardiology, Children's Hospital, Capital Institute of Pediatrics, Beijing, China.

Jiang He 1 Zhang Yi 2 Li Meiting 2 Zhou Huiming 2 Li Jinhao 2 Chen Danlei 2 Li Xiaomei 2*


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
